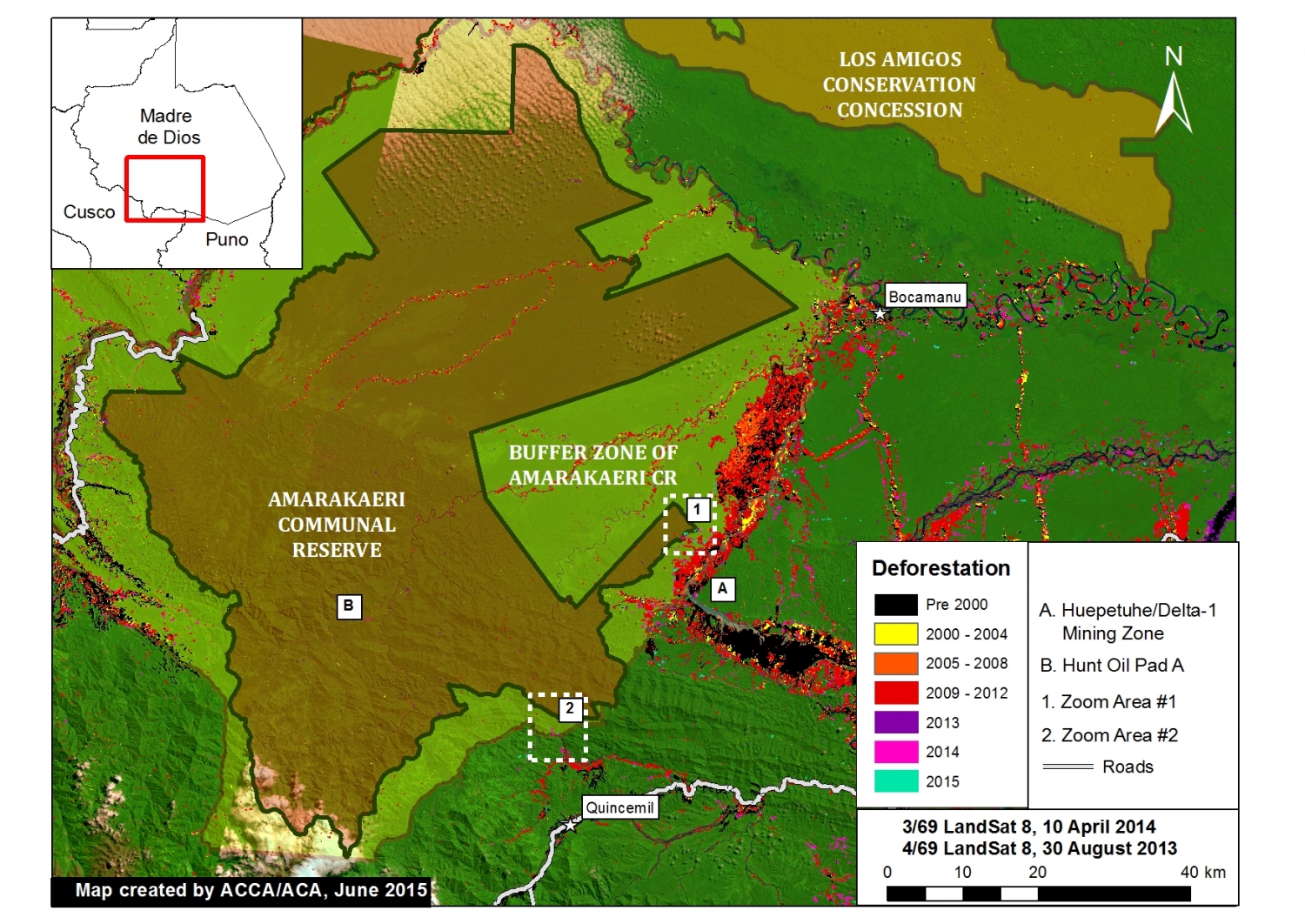
Recall that in Image of the Week #1 and Image of the Week #5 we documented how gold mining deforestation continues to expand within the Department of Madre de Dios, Peru (in the areas known as La Pampa and Upper Malinowski, respectively). Here, Image of the Week #6 documents how expanding deforestation from the mining zone known as Huepetuhe/Delta-1 is now entering the Amarakaeri Communal Reserve, an important Peruvian protected area that is co-managed by indigenous communities and Peru’s National Protected Areas Service (known as SERNANP).
Our analysis shows that gold mining deforestation, expanding from Huepetuhe/Delta-1, entered the southeast corner of the reserve in 2013 and expanded in 2014 and 2015. We also show that gold mining deforestation is spreading within the reserve’s south-eastern buffer zone.
Key Findings:
According to our CLASlite analysis, deforestation entered the southeast corner of the Amarakaeri Communal Reserve in 2013 and expanded in 2014 and 2015 (see Zoom #1 below). Additional analysis revealed that the driver of this deforestation was gold mining due to the pattern and appearance of the forest loss.
We also detected increasing gold mining deforestation within the reserve’s south-eastern buffer zone between 2014 and 2015 (see Zoom #2 below). See below for more details.
We also detected a small amount of deforestation in 2014 from Hunt Oil’s drilling of Pad A within the reserve (see “B” in Image 6a). Note that overall deforestation from this gas exploration project has been very low because the company did not build an access road.
Gold Mining Deforestation Enters the Reserve (Zoom Area #1)
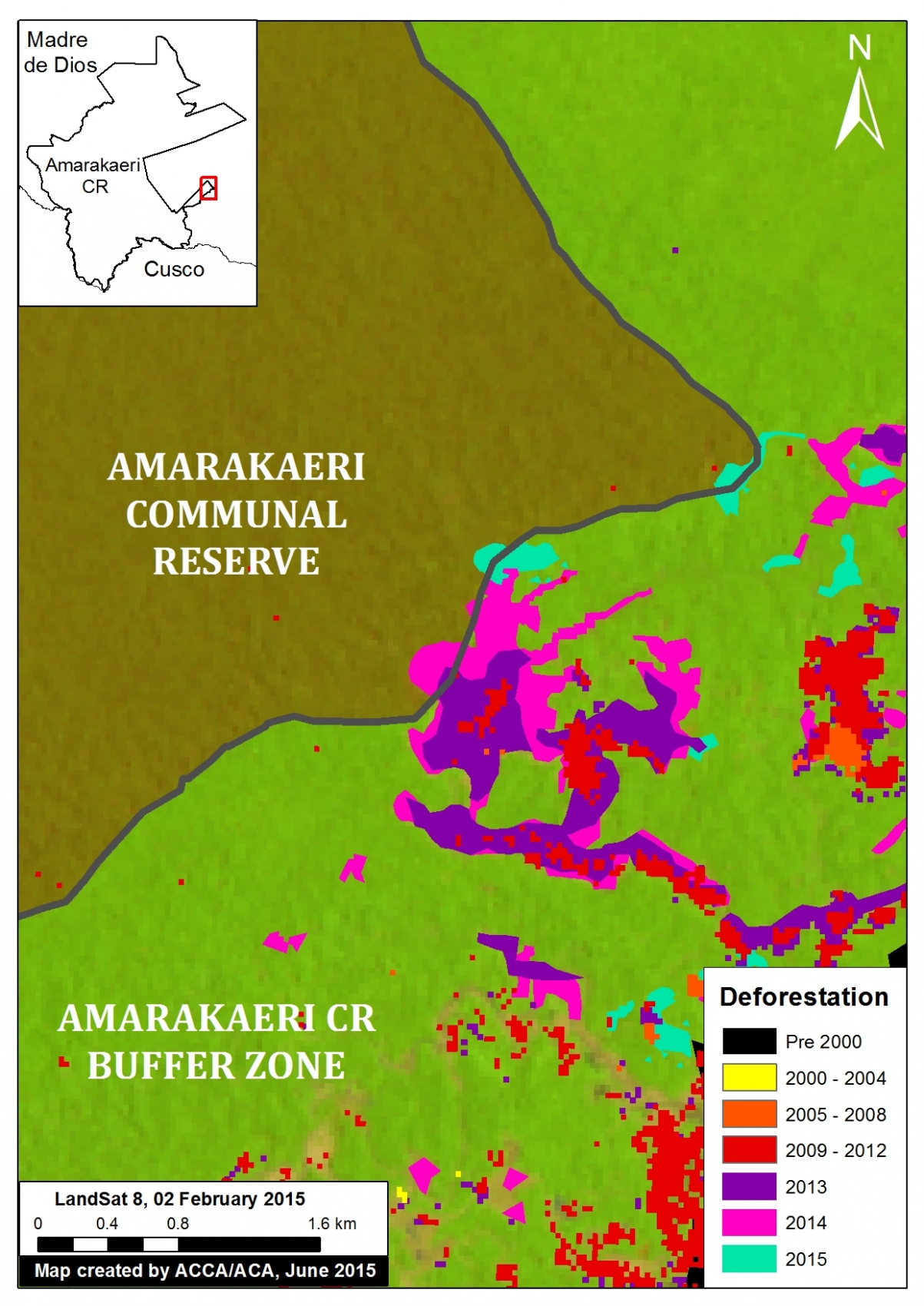
Image 6b is a zoom view of the deforestation within the southeast section of Amarakaeri Communal Reserve and its surrounding buffer zone (see Zoom Area #1 in Image 6a for context).
Here, one can more clearly see how the gold mining deforestation entered the southeast corner of the reserve in 2013 and expanded in 2014 and 2015.
Total gold mining deforestation within this section of the Reserve is currently 11 hectares. Although this is currently only 1% of the Reserve’s total area, it represents a growing trend that may worsen.
Note that all of the rest of the deforestation in the image is within the reserve’s surrounding buffer zone.
Satellite Image Time-series of Deforestation Entering the Reserve (Zoom Area #1)
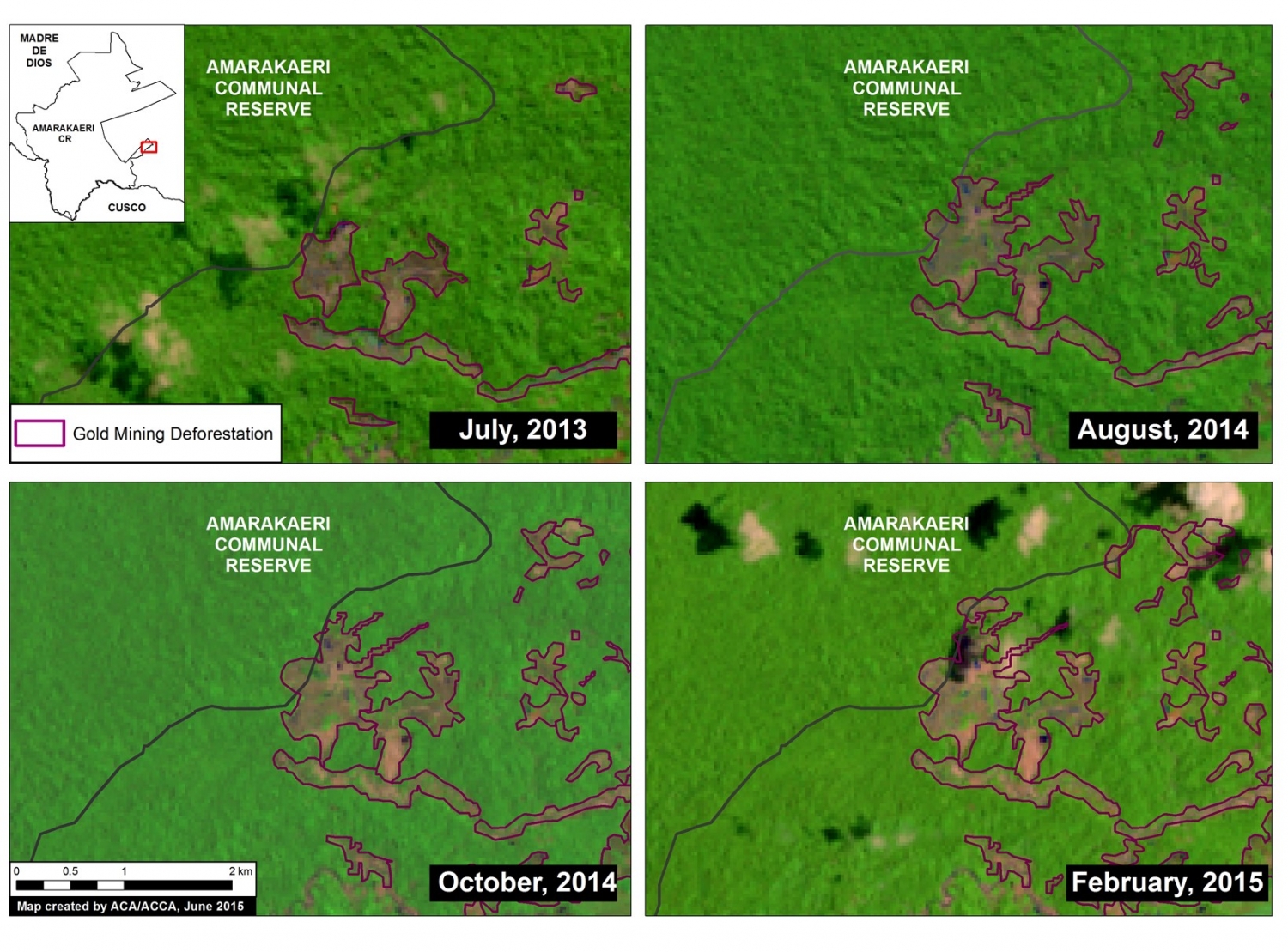
To better understand the deforestation dynamics over time within the southeast corner of the Amarakaeri Communal Reserve, we created a satellite (Landsat 8) image time-series. As seen in Image 6c, gold mining deforestation within the reserve is first seen in July 2013, and then slowly expands on several fronts until February 2015, the last good Landsat image for the area. Note that all four panels show the same location. Also note that all area in each panel outside the reserve is within its official buffer zone.
Gold Mining Deforestation Encroaching Upon Another Part of the Reserve (Zoom Area #2)
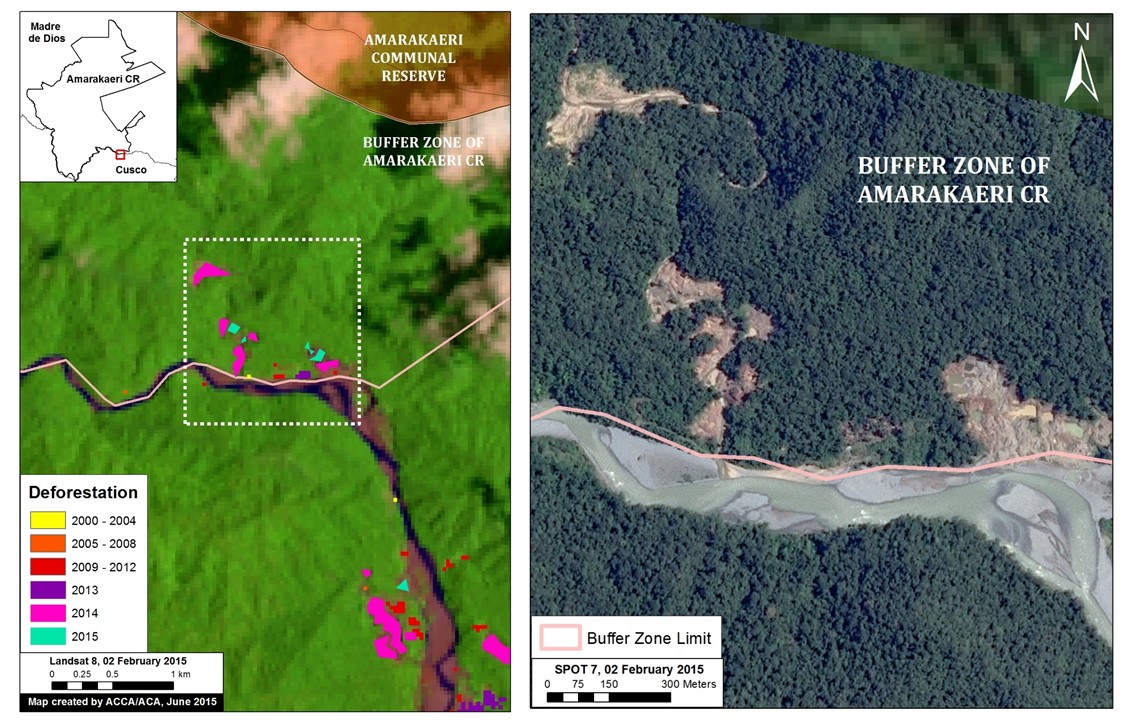
Image 6d shows how gold mining deforestation is encroaching on another part of the south-eastern section of the reserve (see Zoom Area #2 in Image 6a for context). As seen in the left panel, the deforestation within the buffer zone began expanding most notably in 2014 and 2015.
To confirm the driver of the deforestation, we acquired high resolution satellite imagery (SPOT 7 with 1.5 m resolution). As seen in the right panel of Image 6d, the pattern of the recent deforestation is characteristic of gold mining, and not other possible drivers such as agriculture.
Data Description:
Background map is a mosaic of two Landsat 8 images (30 m resolution) from April 10, 2014 and August 30, 2013. Any variation of green indicates forest cover. Note there is some scattered cloud cover. Data is from USGS.
Protected areas data is from SERNANP. Dark green indicates an established Peruvian national protected area or conservation concession and yellow-green indicates an official protected area buffer zone.
Black indicates areas that were deforested as of 2000 according to data from the Peruvian Environment Ministry (MINAM 2009). Yellow, orange, and red indicate areas that were deforested from 2000 to 2012 (each color covers a four year period) (Hansen MC et al. 2013 Science 342: 850–53; Data download).
Purple, pink, and teal indicate areas that were deforested between January 2013 and February 2015 based on our analysis of Landsat imagery using CLASlite forest monitoring software.
Citation
Finer M, Novoa S (2015) Gold Mining Deforestation Enters Amarakaeri Communal Reserve (Madre de Dios, Peru). MAAP: Image #6. Link: https://www.maapprogram.org/2015/08/image-of-the-week-6-gold-mining-deforestation-enters-amarakaeri-communal-reserve/